Calibratable Disambiguation Loss for Multi-Instance Partial-Label Learning
Wei Tang, Yin-Fang Yang, Weijia Zhang, Min-Ling Zhang
https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.17788 https://arxiv.org/pdf/2512.17788 https://arxiv.org/html/2512.17788
arXiv:2512.17788v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Multi-instance partial-label learning (MIPL) is a weakly supervised framework that extends the principles of multi-instance learning (MIL) and partial-label learning (PLL) to address the challenges of inexact supervision in both instance and label spaces. However, existing MIPL approaches often suffer from poor calibration, undermining classifier reliability. In this work, we propose a plug-and-play calibratable disambiguation loss (CDL) that simultaneously improves classification accuracy and calibration performance. The loss has two instantiations: the first one calibrates predictions based on probabilities from the candidate label set, while the second one integrates probabilities from both candidate and non-candidate label sets. The proposed CDL can be seamlessly incorporated into existing MIPL and PLL frameworks. We provide a theoretical analysis that establishes the lower bound and regularization properties of CDL, demonstrating its superiority over conventional disambiguation losses. Experimental results on benchmark and real-world datasets confirm that our CDL significantly enhances both classification and calibration performance.
toXiv_bot_toot
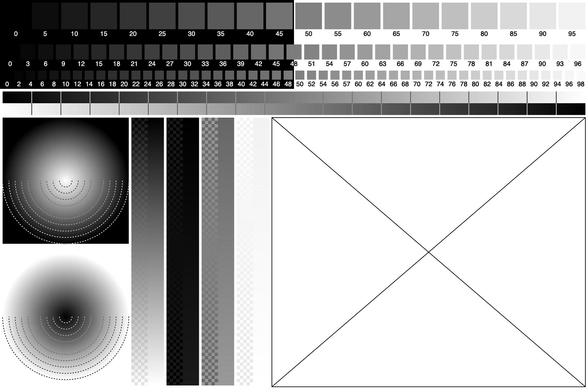
New #ThingUmbrella example to create a parametric, grid layout-based calibration sheet for black and white photography development. The sheet includes different swatches and gradients to measure results/responses of different exposure times and developer solutions/processes. The sheet also includes a placeholder for a custom test image to be added later...
All sheet components are pa…
audacity calibration / rejection therapy & resume refreshes for multipassionate people!
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OusKewz-FxU
This bring me to the second question we had about the paper. Does it suggest hallucinations are a fundamental part of the way we do AI? No. It suggests non-hallucinating models are perfectly possible (if we give up calibration) and it offers a very cheap and simple hack to help us better find them.
Most likely, this has been used behind the scenes by OpenAI for a while, and it's why GPT5 does so much better than 4 in this respect.
Dispersion-Aware Modeling Framework for Parallel Optical Computing
Ziqi Wei, Yuanjian Wan, Yuhu Cheng, Xiao Yu, Peng Xie
https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.18897 https://arxiv.org/pdf/2511.18897 https://arxiv.org/html/2511.18897
arXiv:2511.18897v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Optical computing represents a groundbreaking technology that leverages the unique properties of photons, with innate parallelism standing as its most compelling advantage. Parallel optical computing like cascaded Mach-Zehnder interferometers (MZIs) based offers powerful computational capabilities but also introduces new challenges, particularly concerning dispersion due to the introduction of new frequencies. In this work, we extend existing theories of cascaded MZI systems to develop a generalized model tailored for wavelength-multiplexed parallel optical computing. Our comprehensive model incorporates component dispersion characteristics into a wavelength-dependent transfer matrix framework and is experimentally validated. We propose a computationally efficient compensation strategy that reduces global dispersion error within a 40 nm range from 0.22 to 0.039 using edge-spectrum calibration. This work establishes a fundamental framework for dispersion-aware model and error correction in MZI-based parallel optical computing chips, advancing the reliability of multi-wavelength photonic processors.
toXiv_bot_toot
Crosslisted article(s) found for physics.optics. https://arxiv.org/list/physics.optics/new
[1/1]:
- Robot joint characterisation and control using a magneto-optical rotary encoder
Yunlong Guo, John Canning, Zenon Chaczko, Gang-Ding Peng
https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.17608 https://mastoxiv.page/@arXiv_csRO_bot/115609561523131866
- Comprehensive Multimodal and Multiscale Analysis of Alzheimer Disease in 5xFAD Mice: Optical Spec...
Solanki, Apachigawo, Khan, Maity, Alharthi, Nasim, Poshtiri, Sweety, Xiao, Khan, Pradhan
https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.18320 https://mastoxiv.page/@arXiv_physicsmedph_bot/115609269625501897
- Stable multipole solitons in defocusing saturable media with an annular trapping potential
Xiaoli Lang, Boris A. Malomed, Liangwei Dong
https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.18356 https://mastoxiv.page/@arXiv_nlinPS_bot/115609515016328541
- High-Accuracy Material Classification via Reference-Free Terahertz Spectroscopy: Revisiting Spect...
Mathias Hedegaard Kristensen, Pawe{\l} Piotr Cielecki, Esben Skovsen
https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.18572 https://mastoxiv.page/@arXiv_physicsappph_bot/115609324247942112
- Observation of Dicke cooperativity between strongly coupled phonons and crystal-field excitations...
Fangliang Wu, Xiaoxuan Ma, Zhongwei Zhang, Motoaki Bamba, Jian Sun, Yuan Wan, Shixun Cao, Qi Zhang
https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.18862 https://mastoxiv.page/@arXiv_condmatmtrlsci_bot/115609901666309913
- Strong Energy Dependent Transition Radiation in a Photonic Crystal
V. Gareyan, Zh. Gevorkian
https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.18863 https://mastoxiv.page/@arXiv_physicsaccph_bot/115609494674308155
- 3M-TI: High-Quality Mobile Thermal Imaging via Calibration-free Multi-Camera Cross-Modal Diffusion
Minchong Chen, Xiaoyun Yuan, Junzhe Wan, Jianing Zhang, Jun Zhang
https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.19117 https://mastoxiv.page/@arXiv_csCV_bot/115610498715181168
toXiv_bot_toot