2025-12-12 21:42:07
2026-01-12 12:50:05
We are looking for motivated volunteers to help make #bbuzz a success! Whether you're interested in being a stage host, assisting with registration, or helping with build-up and break-down, we would love to have you on board.
Learn more about our volunteering options: https://2026.berlinbuzzwords.de/helping-hands/
2026-01-13 09:55:44
Gjorde jobbets interaktiva AI utbildning. OM AI vore så smart som de säger har de antagligen inte använt AI för att ta fram underlaget. Först kommer användningsområden som att ex 'analysera saker en inte förstår' senare kommer varningen att AI inte kan värdera svar, att den har bias den inte är medveten om, att den kan hallucinera och att den bara jobbar med sannolikhet - inte förståelse. SEN kommer områden för användning som i anställningsintervjuer, lönesamtal och i framtaganden av…
2025-10-14 08:03:56
Structured Cooperative Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning: a Bayesian Network Perspective
Shahbaz P Qadri Syed, He Bai
https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.09937 https://
2025-10-14 09:29:38
Repeated-and-Offset QPSK for DFT-s-OFDM in Satellite Access
Renaud-Alexandre Pitaval
https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.11445 https://arxiv.org/pdf/2510.11445
2025-10-14 08:59:28
Temporal Cooperative Games
Ashwin Goyal, Drashthi Doshi, Swaprava Nath
https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.11255 https://arxiv.org/pdf/2510.11255
2026-01-09 13:31:37
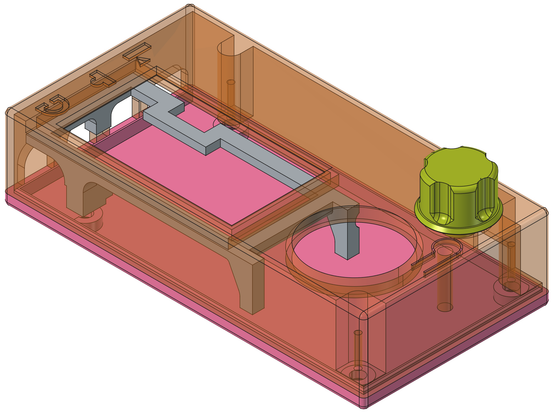
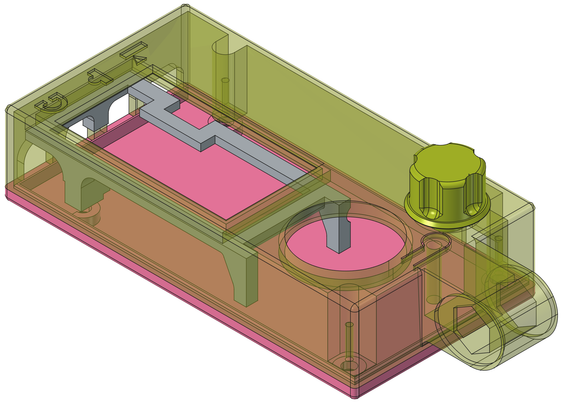
Happy #FreeCADFriday! This week I've been working on re-modelling the case for the Morserino M32 Pocket. At least four different people had worked on the case. It was initially made in FreeCAD, but then was modified with other software, and the current case that QRP Labs is shipping was edited in s…
2025-11-14 09:37:10
S-D-RSM: Stochastic Distributed Regularized Splitting Method for Large-Scale Convex Optimization Problems
Maoran Wang, Xingju Cai, Yongxin Chen
https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.10133 https://arxiv.org/pdf/2511.10133 https://arxiv.org/html/2511.10133
arXiv:2511.10133v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: This paper investigates the problems large-scale distributed composite convex optimization, with motivations from a broad range of applications, including multi-agent systems, federated learning, smart grids, wireless sensor networks, compressed sensing, and so on. Stochastic gradient descent (SGD) and its variants are commonly employed to solve such problems. However, existing algorithms often rely on vanishing step sizes, strong convexity assumptions, or entail substantial computational overhead to ensure convergence or obtain favorable complexity. To bridge the gap between theory and practice, we integrate consensus optimization and operator splitting techniques (see Problem Reformulation) to develop a novel stochastic splitting algorithm, termed the \emph{stochastic distributed regularized splitting method} (S-D-RSM). In practice, S-D-RSM performs parallel updates of proximal mappings and gradient information for only a randomly selected subset of agents at each iteration. By introducing regularization terms, it effectively mitigates consensus discrepancies among distributed nodes. In contrast to conventional stochastic methods, our theoretical analysis establishes that S-D-RSM achieves global convergence without requiring diminishing step sizes or strong convexity assumptions. Furthermore, it achieves an iteration complexity of $\mathcal{O}(1/\epsilon)$ with respect to both the objective function value and the consensus error. Numerical experiments show that S-D-RSM achieves up to 2--3$\times$ speedup compared to state-of-the-art baselines, while maintaining comparable or better accuracy. These results not only validate the algorithm's theoretical guarantees but also demonstrate its effectiveness in practical tasks such as compressed sensing and empirical risk minimization.
toXiv_bot_toot
2025-10-14 09:15:48
Fluidity and morphological stability of an amorphous thin film with radiation-induced defect kinetics
Tyler P. Evans, Eden Heyen
https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.10745 https://…
2025-11-11 06:57:02
GCVE-BCP-05 - GCVE Vulnerability Format (Updated CVE Record Format) has been published as DRAFT and ready for public review.
The standard is similar to the @… record format with some extensions (via the X_ prefixes) for GCVE format and the reference implementation vulnerability-lookup. This allows some flexibility and innovation in GNA - GCVE space w…