On Dynamic Programming Theory for Leader-Follower Stochastic Games
Jilles Steeve Dibangoye, Thibaut Le Marre, Ocan Sankur, Fran\c{c}ois Schwarzentruber
https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.05667 https://arxiv.org/pdf/2512.05667 https://arxiv.org/html/2512.05667
arXiv:2512.05667v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Leader-follower general-sum stochastic games (LF-GSSGs) model sequential decision-making under asymmetric commitment, where a leader commits to a policy and a follower best responds, yielding a strong Stackelberg equilibrium (SSE) with leader-favourable tie-breaking. This paper introduces a dynamic programming (DP) framework that applies Bellman recursion over credible sets-state abstractions formally representing all rational follower best responses under partial leader commitments-to compute SSEs. We first prove that any LF-GSSG admits a lossless reduction to a Markov decision process (MDP) over credible sets. We further establish that synthesising an optimal memoryless deterministic leader policy is NP-hard, motivating the development of {\epsilon}-optimal DP algorithms with provable guarantees on leader exploitability. Experiments on standard mixed-motive benchmarks-including security games, resource allocation, and adversarial planning-demonstrate empirical gains in leader value and runtime scalability over state-of-the-art methods.
toXiv_bot_toot
"For others, the exploration of old computer magazines brings the possibility of running old software. Many computer magazines, and not only the programming kind, used to bundle reams of source code listings across their pages, and many an enthusiast would painstakingly type those code bits by hand, in order to have a new utility, to learn a new programming language, or to enjoy a new game."
This is so niche and yet so relevant to my interests: "Kip is an experimental programming language that combines Turkish grammar rules with a type system. Case endings, vowel harmony, and other Turkish morphological features are an integral part of Kip's type-checking process."
https://github.com/kip-dili/kip/…
Multi-port programmable silicon photonics using low-loss phase change material Sb$_2$Se$_3$
Thomas W. Radford, Idris A Ajia, Latif Rozaqi, Priya Deoli, Xingzhao Yan, Mehdi Banakar, David J Thomson, Ioannis Zeimpekis, Alberto Politi, Otto L. Muskens
https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.18205 https://arxiv.org/pdf/2511.18205 https://arxiv.org/html/2511.18205
arXiv:2511.18205v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Reconfigurable photonic devices are rapidly emerging as a cornerstone of next generation optical technologies, with wide ranging applications in quantum simulation, neuromorphic computing, and large-scale photonic processors. A central challenge in this field is identifying an optimal platform to enable compact, efficient, and scalable reconfigurability. Optical phase-change materials (PCMs) offer a compelling solution by enabling non-volatile, reversible tuning of optical properties, compatible with a wide range of device platforms and current CMOS technologies. In particular, antimony tri-selenide ($\text{Sb}_{2}\text{Se}_{3}$) stands out for its ultra low-loss characteristics at telecommunication wavelengths and its reversible switching. In this work, we present an experimental platform capable of encoding multi-port operations onto the transmission matrix of a compact multimode interferometer architecture on standard 220~nm silicon photonics using \textit{in-silico} designed digital patterns. The multi-port devices are clad with a thin film of $\text{Sb}_{2}\text{Se}_{3}$, which can be optically addressed using direct laser writing to provide local perturbations to the refractive index. A range of multi-port geometries from 2$\times$2 up to 5$\times$5 couplers are demonstrated, achieving simultaneous control of up to 25 matrix elements with programming accuracy of 90% relative to simulated patterns. Patterned devices remain stable with consistent optical performance across the C-band wavelengths. Our work establishes a pathway towards the development of large scale PCM-based reconfigurable multi-port devices which will allow implementing matrix operations on three orders of magnitude smaller areas than interferometer meshes.
toXiv_bot_toot
Verification of Sequential Convex Programming for Parametric Non-convex Optimization
Rajiv Sambharya, Nikolai Matni, George Pappas
https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.10622 https://arxiv.org/pdf/2511.10622 https://arxiv.org/html/2511.10622
arXiv:2511.10622v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: We introduce a verification framework to exactly verify the worst-case performance of sequential convex programming (SCP) algorithms for parametric non-convex optimization. The verification problem is formulated as an optimization problem that maximizes a performance metric (e.g., the suboptimality after a given number of iterations) over parameters constrained to be in a parameter set and iterate sequences consistent with the SCP update rules. Our framework is general, extending the notion of SCP to include both conventional variants such as trust-region, convex-concave, and prox-linear methods, and algorithms that combine convex subproblems with rounding steps, as in relaxing and rounding schemes. Unlike existing analyses that may only provide local guarantees under limited conditions, our framework delivers global worst-case guarantees--quantifying how well an SCP algorithm performs across all problem instances in the specified family. Applications in control, signal processing, and operations research demonstrate that our framework provides, for the first time, global worst-case guarantees for SCP algorithms in the parametric setting.
toXiv_bot_toot
Easy Adaptation: An Efficient Task-Specific Knowledge Injection Method for Large Models in Resource-Constrained Environments
Dong Chen, Zhengqing Hu, Shixing Zhao, Yibo Guo
https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.17771 https://arxiv.org/pdf/2512.17771 https://arxiv.org/html/2512.17771
arXiv:2512.17771v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: While the enormous parameter scale endows Large Models (LMs) with unparalleled performance, it also limits their adaptability across specific tasks. Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) has emerged as a critical approach for effectively adapting LMs to a diverse range of downstream tasks. However, existing PEFT methods face two primary challenges: (1) High resource cost. Although PEFT methods significantly reduce resource demands compared to full fine-tuning, it still requires substantial time and memory, making it impractical in resource-constrained environments. (2) Parameter dependency. PEFT methods heavily rely on updating a subset of parameters associated with LMs to incorporate task-specific knowledge. Yet, due to increasing competition in the LMs landscape, many companies have adopted closed-source policies for their leading models, offering access only via Application Programming Interface (APIs). Whereas, the expense is often cost-prohibitive and difficult to sustain, as the fine-tuning process of LMs is extremely slow. Even if small models perform far worse than LMs in general, they can achieve superior results on particular distributions while requiring only minimal resources. Motivated by this insight, we propose Easy Adaptation (EA), which designs Specific Small Models (SSMs) to complement the underfitted data distribution for LMs. Extensive experiments show that EA matches the performance of PEFT on diverse tasks without accessing LM parameters, and requires only minimal resources.
toXiv_bot_toot
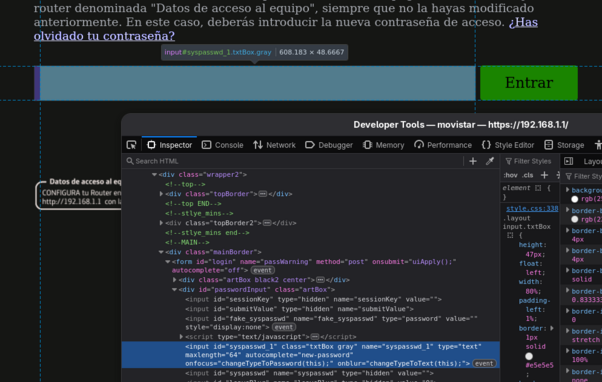
In Today's programming woes consumer grade equipment being mediocre.
I wondered why my password manager didn't work with the input of the ISP router's login. Turns out it declares the `<input>` as `type=text` and changes it between `password` and `text` on focus. Also uses the `autofill=new-password` attribute wrong, should be `current-password`.
Locally Linear Convergence for Nonsmooth Convex Optimization via Coupled Smoothing and Momentum
Reza Rahimi Baghbadorani, Sergio Grammatico, Peyman Mohajerin Esfahani
https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.10239 https://arxiv.org/pdf/2511.10239 https://arxiv.org/html/2511.10239
arXiv:2511.10239v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: We propose an adaptive accelerated smoothing technique for a nonsmooth convex optimization problem where the smoothing update rule is coupled with the momentum parameter. We also extend the setting to the case where the objective function is the sum of two nonsmooth functions. With regard to convergence rate, we provide the global (optimal) sublinear convergence guarantees of O(1/k), which is known to be provably optimal for the studied class of functions, along with a local linear rate if the nonsmooth term fulfills a so-call locally strong convexity condition. We validate the performance of our algorithm on several problem classes, including regression with the l1-norm (the Lasso problem), sparse semidefinite programming (the MaxCut problem), Nuclear norm minimization with application in model free fault diagnosis, and l_1-regularized model predictive control to showcase the benefits of the coupling. An interesting observation is that although our global convergence result guarantees O(1/k) convergence, we consistently observe a practical transient convergence rate of O(1/k^2), followed by asymptotic linear convergence as anticipated by the theoretical result. This two-phase behavior can also be explained in view of the proposed smoothing rule.
toXiv_bot_toot
Beyond Revenue and Welfare: Counterfactual Analysis of Spectrum Auctions with Application to Canada's 3800MHz Allocation
Sara Jalili Shani, Kris Joseph, Michael B. McNally, James R. Wright
https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.08106 https://arxiv.org/pdf/2512.08106 https://arxiv.org/html/2512.08106
arXiv:2512.08106v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Spectrum auctions are the primary mechanism through which governments allocate scarce radio frequencies, with outcomes that shape competition, coverage, and innovation in telecommunications markets. While traditional models of spectrum auctions often rely on strong equilibrium assumptions, we take a more parsimonious approach by modeling bidders as myopic and straightforward: in each round, firms simply demand the bundle that maximizes their utility given current prices. Despite its simplicity, this model proves effective in predicting the outcomes of Canada's 2023 auction of 3800 MHz spectrum licenses. Using detailed round-by-round bidding data, we estimate bidders' valuations through a linear programming framework and validate that our model reproduces key features of the observed allocation and price evolution. We then use these estimated valuations to simulate a counterfactual auction under an alternative mechanism that incentivizes deployment in rural and remote regions, aligning with one of the key objectives set out in the Canadian Telecommunications Act. The results show that the proposed mechanism substantially improves population coverage in underserved areas. These findings demonstrate that a behavioral model with minimal assumptions is sufficient to generate reliable counterfactual predictions, making it a practical tool for policymakers to evaluate how alternative auction designs may influence future outcomes. In particular, our study demonstrates a method for counterfactual mechanism design, providing a framework to evaluate how alternative auction rules could advance policy goals such as equitable deployment across Canada.
toXiv_bot_toot