2025-12-15 14:18:15
'systemd-analyze' is a useful if random tool that's part of systemd; it's actually got a whole bunch of different useful bits thrown in. The 'blame' , 'plot' and 'critical-chain' subcommands let you debug start up time. 'calendar' and 'timestamp' let you test if your format for a time/date is OK to use in a systemd file; 'verify' lets you check your systemd unit file for errors. There's loads more random bits.
2026-01-16 16:01:40
Analysis: Colossus 2, one of the world's largest AI datacenters, will use as much water/year as 2.5 average In-N-Outs, assuming only drinkable water and burgers (SemiAnalysis)
https://newsletter.semianalysis.com/p/from-tokens-to-burgers-a-water-footprint
2025-12-13 06:56:25
┬źÔÇťOne SIM card can be used for hundreds of different platforms,ÔÇŁ said Dek. ÔÇťVendors recoup SIM costs by selling high-demand verifications for apps like Facebook and Telegram, then profit from the long tail of other platforms.ÔÇŁ
Additional analyses show global stocks of fake accounts are highest for platforms such as X, Uber, Discord, Amazon, Tinder and gaming platform Steam┬╗
#FakeProfiles
2025-11-14 09:35:40
An inexact semismooth Newton-Krylov method for semilinear elliptic optimal control problem
Shiqi Chen, Xuesong Chen
https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.10058 https://arxiv.org/pdf/2511.10058 https://arxiv.org/html/2511.10058
arXiv:2511.10058v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: An inexact semismooth Newton method has been proposed for solving semi-linear elliptic optimal control problems in this paper. This method incorporates the generalized minimal residual (GMRES) method, a type of Krylov subspace method, to solve the Newton equations and utilizes nonmonotonic line search to adjust the iteration step size. The original problem is reformulated into a nonlinear equation through variational inequality principles and discretized using a second-order finite difference scheme. By leveraging slanting differentiability, the algorithm constructs semismooth Newton directions and employs GMRES method to inexactly solve the Newton equations, significantly reducing computational overhead. A dynamic nonmonotonic line search strategy is introduced to adjust stepsizes adaptively, ensuring global convergence while overcoming local stagnation. Theoretical analysis demonstrates that the algorithm achieves superlinear convergence near optimal solutions when the residual control parameter $\eta_k$ approaches to 0. Numerical experiments validate the method's accuracy and efficiency in solving semilinear elliptic optimal control problems, corroborating theoretical insights.
toXiv_bot_toot
2025-11-04 09:10:54
Ab 2027 will die niederl├Ąndische Regierung gro├če #Photovoltaik-Anlagen ├╝ber zweiseitige #Differenzvertr├Ąge f├Ârdern.
Entwickler erhalten einen festen Verg├╝tungspreis. Liegt der #Strompreis
2025-12-10 08:38:00
Manifolds and Modules: How Function Develops in a Neural Foundation Model
Johannes Bertram, Luciano Dyballa, T. Anderson Keller, Savik Kinger, Steven W. Zucker
https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.07869 https://arxiv.org/pdf/2512.07869 https://arxiv.org/html/2512.07869
arXiv:2512.07869v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Foundation models have shown remarkable success in fitting biological visual systems; however, their black-box nature inherently limits their utility for under- standing brain function. Here, we peek inside a SOTA foundation model of neural activity (Wang et al., 2025) as a physiologist might, characterizing each 'neuron' based on its temporal response properties to parametric stimuli. We analyze how different stimuli are represented in neural activity space by building decoding man- ifolds, and we analyze how different neurons are represented in stimulus-response space by building neural encoding manifolds. We find that the different processing stages of the model (i.e., the feedforward encoder, recurrent, and readout modules) each exhibit qualitatively different representational structures in these manifolds. The recurrent module shows a jump in capabilities over the encoder module by 'pushing apart' the representations of different temporal stimulus patterns; while the readout module achieves biological fidelity by using numerous specialized feature maps rather than biologically plausible mechanisms. Overall, we present this work as a study of the inner workings of a prominent neural foundation model, gaining insights into the biological relevance of its internals through the novel analysis of its neurons' joint temporal response patterns.
toXiv_bot_toot
2026-01-01 12:42:01
from my link log ÔÇö
Destroying x86_64 instruction decoders with differential fuzzing.
https://blog.trailofbits.com/2019/10/31/destroying-x86_64-instruction-decoders-with-differential-fuzzing/
saved 2019-10-31
2026-01-05 19:31:05
One of the strongest factors in building and motivating an organization as a leader is saying out loud regularly that you care about people.
As Alicja frames, it's the difference between knowing what ice cream tastes like and actually eating ice cream.
It is so SO meaningful to tell people that you care about them, that you value their expertise and work, that they deserve to be respected and supported, and so on. Customize it to the individual situation: identify what someoÔÇŽ
2025-11-11 19:03:35
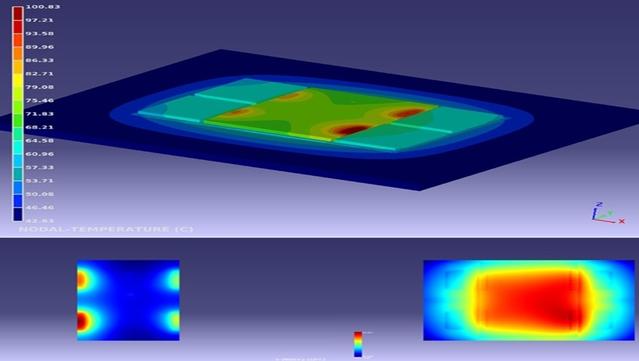
čŹö Thermal, Mechanical, And Material Stresses Grow With Die Stacking
https://semiengineering.com/thermal-mechanical-and-material-stresses-grow-with-die-stacking/
2026-01-05 15:16:45
In #Dorfen wurde ein neuer #Solarpark mit #Stromspeicher feierlich in Betrieb genommen.
Die Anlage versorgt rund 1.200 Haushalte und stabilisiert durch gezielte Einspeisung das