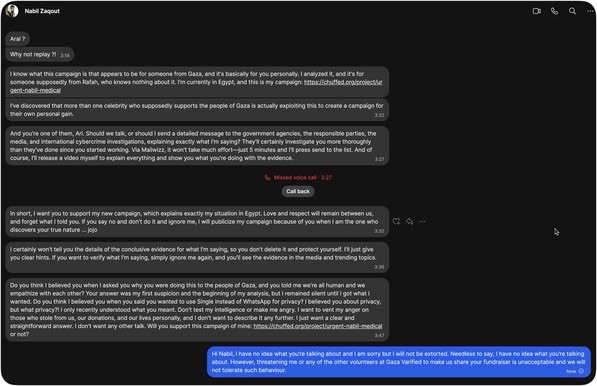
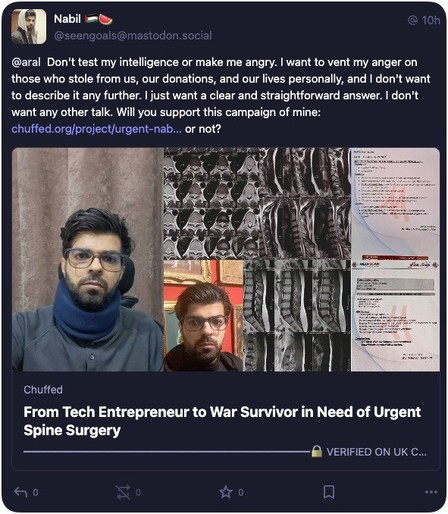
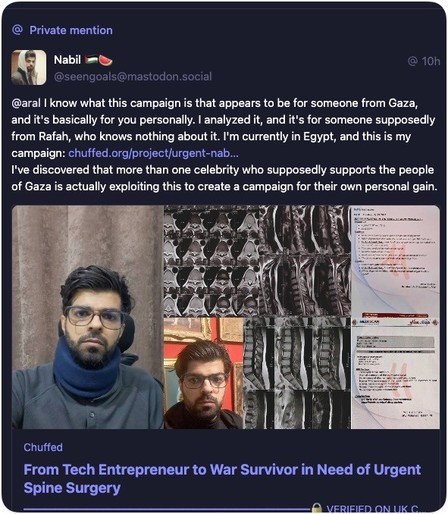
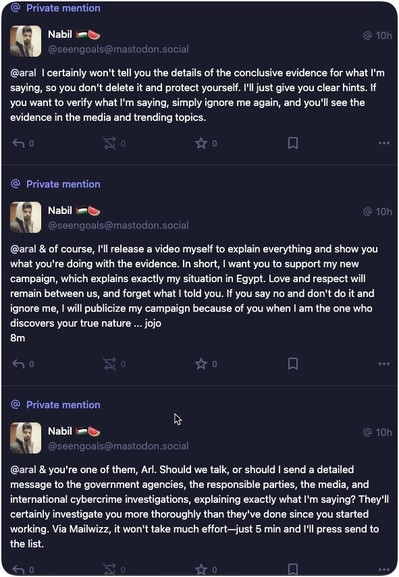
Content warning: ICE, racism, police brutality
Also: we're seeing what happens when white people are actually motivated en-masse (and the George Floyd response was actually another decent example of this).
General strike -> capitalist class goes "oh shit we need to deescalate" -> temporary reprieve.
White people actually putting their bodies on the line (or at least near enough to it that ICE killed them) got results. This is direct evidence of just how much oppression depends on the social fragmentation it invests immense energy into creating in order to not get its ass kicked both ideologically and literally.
Also for those white people like me who are scared to participate: I don't have the numbers, but there were something like 50,000 people who stood up (even if we just want to count observers and joiners-of-whistle-crowds I'd guess at least 5,000-10,000). Two in that category died (more like 30 have died in the direct-targets-of-ICE category). So don't look at Pretti and think "protesting is so risky." Consider that both the odds of being the one or two killed are low, and that if you don't stand up quickly and strongly enough against this shit, the body count will grow much higher.
This isn't over, and continued escalation and resistance is super critical now. Rather than hoping the twin cities story is a story of heroes elsewhere who solved the problem, make it a story of an inspiring example that gets replicated in LA, Chicago, and all around the nation where ICE is trying to metastasize into an unaccountable secret police.