2025-12-29 03:14:07
Kiedy spałeś jeszcze krócej niż zwykle, bo tuż przed snem wpadłeś na to, jak zaimplementować mnożenie w https://nandgame.com.
Oczywiście, jak już się położyłeś, to wpadłeś na to, jak zrobić to szybciej, i z 32-bitowym wynikiem. Aczkolwiek stara metoda też dobra, taka ładnie pedagogiczna.
2025-12-11 14:46:51
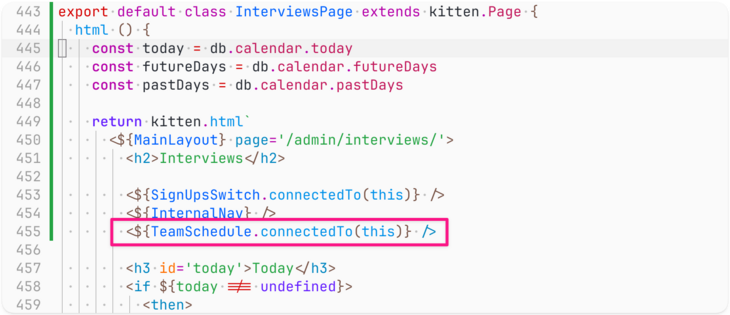
I love how simple Kitten’s Streaming HTML workflow makes building features like this, especially when using class-based Kitten pages and components :)
#Kitten
2026-01-19 19:15:02
Hello Stranger?
I took this photo recently on a hike on one of my local hills when I turned around and saw a stranger walking there.
I hardly ever have people in my photos, because I don't WANT people there. But this scene was so different.
The fog was just thick enough to see the person, yet I didn't feel like the person was "near". It all just felt so distant.
#hiking
2025-12-22 10:34:10
Exploiting ID-Text Complementarity via Ensembling for Sequential Recommendation
Liam Collins, Bhuvesh Kumar, Clark Mingxuan Ju, Tong Zhao, Donald Loveland, Leonardo Neves, Neil Shah
https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.17820 https://arxiv.org/pdf/2512.17820 https://arxiv.org/html/2512.17820
arXiv:2512.17820v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: Modern Sequential Recommendation (SR) models commonly utilize modality features to represent items, motivated in large part by recent advancements in language and vision modeling. To do so, several works completely replace ID embeddings with modality embeddings, claiming that modality embeddings render ID embeddings unnecessary because they can match or even exceed ID embedding performance. On the other hand, many works jointly utilize ID and modality features, but posit that complex fusion strategies, such as multi-stage training and/or intricate alignment architectures, are necessary for this joint utilization. However, underlying both these lines of work is a lack of understanding of the complementarity of ID and modality features. In this work, we address this gap by studying the complementarity of ID- and text-based SR models. We show that these models do learn complementary signals, meaning that either should provide performance gain when used properly alongside the other. Motivated by this, we propose a new SR method that preserves ID-text complementarity through independent model training, then harnesses it through a simple ensembling strategy. Despite this method's simplicity, we show it outperforms several competitive SR baselines, implying that both ID and text features are necessary to achieve state-of-the-art SR performance but complex fusion architectures are not.
toXiv_bot_toot
2025-11-16 00:36:40
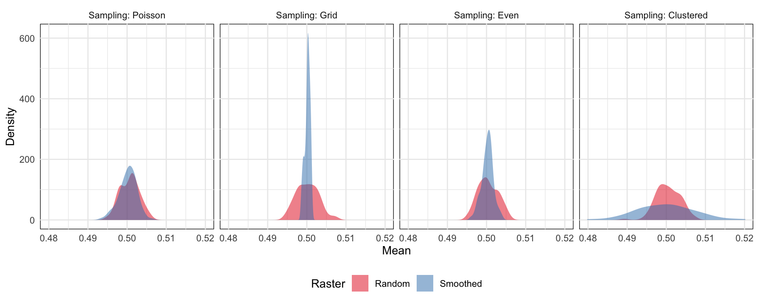
How spatial sampling methods affect the variance of your mean estimate when spatial autocorrelation is present.
https://dosull.github.io/posts/2025-11-14-gia-chapter-2A-spatial-autocorrelation/
2026-01-07 09:55:53
ENDA en tekst fra #Toje i #Aftenposten. Nå prŸver han å skille mellom deskriptive analyser og normative, politiske lŸsninger. Men han overser glatt at hans forsŸk på deskriptive "analyser" er så mettet med normativt ladede begreper, premisser og vinklinger at svaret hans ikke holder vann.
2025-11-14 09:39:30
Halpern Acceleration of the Inexact Proximal Point Method of Rockafellar
Liwei Zhang, Fanli Zhuang, Ning Zhang
https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.10372 https://arxiv.org/pdf/2511.10372 https://arxiv.org/html/2511.10372
arXiv:2511.10372v1 Announce Type: new
Abstract: This paper investigates a Halpern acceleration of the inexact proximal point method for solving maximal monotone inclusion problems in Hilbert spaces. The proposed Halpern inexact proximal point method (HiPPM) is shown to be globally convergent, and a unified framework is developed to analyze its worst-case convergence rate. Under mild summability conditions on the inexactness tolerances, HiPPM achieves an $\mathcal{O}(1/k^{2})$ rate in terms of the squared fixed-point residual. Furthermore, under additional mild condition, the method retains a fast linear convergence rate. Building upon this framework, we further extend the acceleration technique to constrained convex optimization through the augmented Lagrangian formulation. In analogy to Rockafellar's classical results, the resulting accelerated inexact augmented Lagrangian method inherits the convergence rate and complexity guarantees of HiPPM. The analysis thus provides a unified theoretical foundation for accelerated inexact proximal algorithms and their augmented Lagrangian extensions.
toXiv_bot_toot
2025-11-03 03:54:49
I had a couple folks hop into our Discord to ask for some help on the ARK Server installation script.
Got them resolved, but one of the comments struck me as interesting. "Do you support modded maps"
I didn't even think of modded maps... but that sounded like a good idea!
So I'd like to announce my Debian/Ubuntu installer for ARK SA now has support for modded maps! (and a bunch of other improvements to the UI)
2026-01-18 14:47:47
Some photos from today's hike in the mountains. To escape the fog.
It was very very icy at the bottom. And I was super happy to have my micro spikes.
The way up was pretty calm. Right the #silentsunday I had desired. At the summit there were a bit too many people and I didn't see proper motives. So I just enjoyed the view and the really warm temperature.
On the wa…
2025-12-22 13:54:55
Replaced article(s) found for cs.LG. https://arxiv.org/list/cs.LG/new
[4/5]:
- Sample, Don't Search: Rethinking Test-Time Alignment for Language Models
Gon\c{c}alo Faria, Noah A. Smith
https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.03790 https://mastoxiv.page/@arXiv_csCL_bot/114301112970577326
- A Survey on Archetypal Analysis
Aleix Alcacer, Irene Epifanio, Sebastian Mair, Morten M{\o}rup
https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.12392 https://mastoxiv.page/@arXiv_statME_bot/114357826909813483
- The Stochastic Occupation Kernel (SOCK) Method for Learning Stochastic Differential Equations
Michael L. Wells, Kamel Lahouel, Bruno Jedynak
https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.11622 https://mastoxiv.page/@arXiv_statML_bot/114539065460187982
- BOLT: Block-Orthonormal Lanczos for Trace estimation of matrix functions
Kingsley Yeon, Promit Ghosal, Mihai Anitescu
https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.12289 https://mastoxiv.page/@arXiv_mathNA_bot/114539035462135281
- Clustering and Pruning in Causal Data Fusion
Otto Tabell, Santtu Tikka, Juha Karvanen
https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.15215 https://mastoxiv.page/@arXiv_statML_bot/114550346291754635
- On the performance of multi-fidelity and reduced-dimensional neural emulators for inference of ph...
Chloe H. Choi, Andrea Zanoni, Daniele E. Schiavazzi, Alison L. Marsden
https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.11683 https://mastoxiv.page/@arXiv_statML_bot/114692410563481289
- Beyond Force Metrics: Pre-Training MLFFs for Stable MD Simulations
Maheshwari, Tang, Ock, Kolluru, Farimani, Kitchin
https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.14850 https://mastoxiv.page/@arXiv_physicschemph_bot/114709402590755731
- Quantifying Uncertainty in the Presence of Distribution Shifts
Yuli Slavutsky, David M. Blei
https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.18283 https://mastoxiv.page/@arXiv_statML_bot/114738165218533987
- ZKPROV: A Zero-Knowledge Approach to Dataset Provenance for Large Language Models
Mina Namazi, Alexander Nemecek, Erman Ayday
https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.20915 https://mastoxiv.page/@arXiv_csCR_bot/114754394485208892
- SpecCLIP: Aligning and Translating Spectroscopic Measurements for Stars
Zhao, Huang, Xue, Kong, Liu, Tang, Beers, Ting, Luo
https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.01939 https://mastoxiv.page/@arXiv_astrophIM_bot/114788369702591337
- Towards Facilitated Fairness Assessment of AI-based Skin Lesion Classifiers Through GenAI-based I...
Ko Watanabe, Stanislav Frolov, Aya Hassan, David Dembinsky, Adriano Lucieri, Andreas Dengel
https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.17860 https://mastoxiv.page/@arXiv_csCV_bot/114912976717523345
- PASS: Probabilistic Agentic Supernet Sampling for Interpretable and Adaptive Chest X-Ray Reasoning
Yushi Feng, Junye Du, Yingying Hong, Qifan Wang, Lequan Yu
https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.10501 https://mastoxiv.page/@arXiv_csAI_bot/115032101532614110
- Unified Acoustic Representations for Screening Neurological and Respiratory Pathologies from Voice
Ran Piao, Yuan Lu, Hareld Kemps, Tong Xia, Aaqib Saeed
https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.20717 https://mastoxiv.page/@arXiv_csSD_bot/115111255835875066
- Machine Learning-Driven Predictive Resource Management in Complex Science Workflows
Tasnuva Chowdhury, et al.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.11512 https://mastoxiv.page/@arXiv_csDC_bot/115213444524490263
- MatchFixAgent: Language-Agnostic Autonomous Repository-Level Code Translation Validation and Repair
Ali Reza Ibrahimzada, Brandon Paulsen, Reyhaneh Jabbarvand, Joey Dodds, Daniel Kroening
https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.16187 https://mastoxiv.page/@arXiv_csSE_bot/115247172280557686
- Automated Machine Learning Pipeline: Large Language Models-Assisted Automated Dataset Generation ...
Adam Lahouari, Jutta Rogal, Mark E. Tuckerman
https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.21647 https://mastoxiv.page/@arXiv_condmatmtrlsci_bot/115286737423175311
- Quantifying the Impact of Structured Output Format on Large Language Models through Causal Inference
Han Yuan, Yue Zhao, Li Zhang, Wuqiong Luo, Zheng Ma
https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.21791 https://mastoxiv.page/@arXiv_csCL_bot/115287166674809413
- The Generation Phases of Flow Matching: a Denoising Perspective
Anne Gagneux, S\'egol\`ene Martin, R\'emi Gribonval, Mathurin Massias
https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.24830 https://mastoxiv.page/@arXiv_csCV_bot/115462527449411627
- Data-driven uncertainty-aware seakeeping prediction of the Delft 372 catamaran using ensemble Han...
Giorgio Palma, Andrea Serani, Matteo Diez
https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.04461 https://mastoxiv.page/@arXiv_eessSY_bot/115507785247809767
- Generalized infinite dimensional Alpha-Procrustes based geometries
Salvish Goomanee, Andi Han, Pratik Jawanpuria, Bamdev Mishra
https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.09801 https://mastoxiv.page/@arXiv_statML_bot/115547135711272091
toXiv_bot_toot
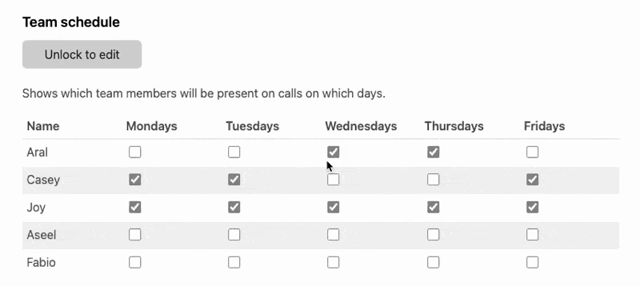
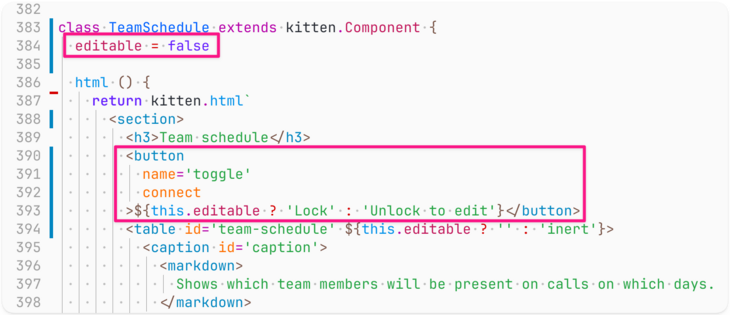
![Screenshot of code, continuation of the same class, starting with the end of the html() method from the previous screenshot and going till the end of the class (the table[inert] style and the onToggle() method are highlighted:
<style>
table[inert] {
opacity: 0.9;
filter: grayscale(100%);
}
</style>
</table>
</section>
`
}
onToggle () {
this.editable = !this.editable
console.log(this.editable)…](https://s3-eu-central-1.amazonaws.com/mastodon-aral/media_attachments/files/115/701/475/591/066/309/small/0dd9da4ffbc5e31c.png)