2026-01-01 13:32:31
You’d think people who post “I asked AI to help me with [thing] but for some reason what it said didn’t work” reflect on their experience.
But no, most will use it over and over again.
The reason for this is that it’s designed to be an obsequious and sycophantic slave-simulator and people get high on the perceived power dynamic.
Truly a remarkable grift.
2025-11-23 15:10:54
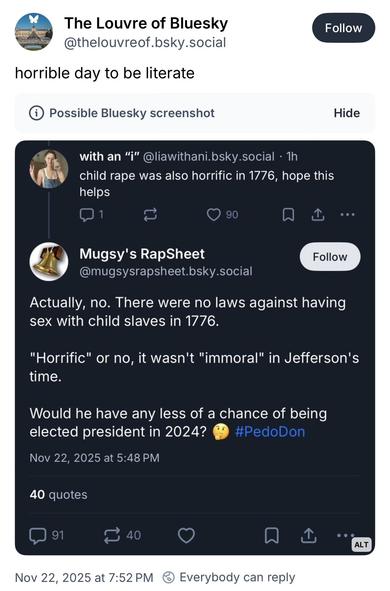
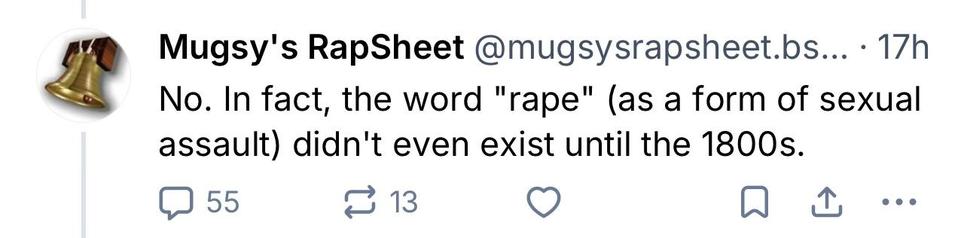
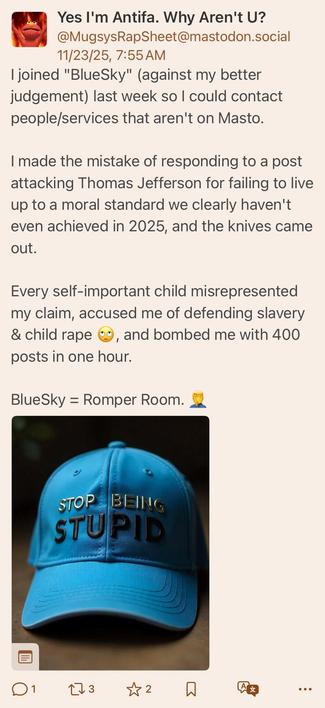
Yea I can’t imagine why anyone thought this dipshit was defending rape…I mean aside from the over half a dozen posts where he defended rape as “not immoral”, literally said “No. In fact, the word "rape"…didn't even exist until the 1800s.” and arguing that being “owned”* wasn’t “horrific”
Complete mystery why people went after him, must be some weird BlueSky thing. 😂
JFC
2025-11-21 08:32:29
2025-11-13 22:10:04
One other pattern that I kept experiencing last year when I was actually trying these tools in my work (because I had so many people pushing them on me I started to think I was crazy):
Them: “oh you are struggling with X? I have been using AI to solve it and it gives me the solution in less than 10 minutes! You HAVE TO try it!”
Me: “X is really annoying, I’d love to get help with it. I’ll try that, thanks!”
* I go and try to do X, spend hours prompting AI back-and-forth as it keeps messing up and doing things wrong. I give up and do the thing manually, spending 2-3x the time I would have spent if I did it myself from the start.*
*days / weeks later*
Me: “hey, person, I tried to do X with AI and it didn’t work. I kept getting issues like Y and Z. Did I prompt it wrong? This is what I tried.”
Them: *nods, maybe chuckles* “oh yeah, it does that. I still haven’t been able to figure out how to reliably do X. I tend to redo the output completely too. But sometimes it helps me do like this tiny part. Anyway, these tools will improve soon and we won’t have to do so many manual revisions. “
I kid you not, this stuff happened every other week.
#AI #LLMs #work #tech #AIBubble